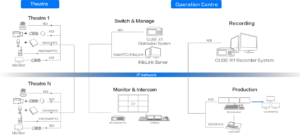
Video encoder as the sending end of the video source, is a device that integrates collection, encoding, compression, and transmission. Most of them support multiple network transmission protocols such as TS/HLS/FLV/RTSP/RTMP/UDP/RTP/unicast/multicast. They are an important component of the digital network video and audio live broadcast system. See What is a video encoder?
In video transmission we have hardware encoder and software encoder. The biggest difference between a hardware encoder and software encoder is that hardware encoders are purpose-built devices with dedicated and more professional processing uses GPU (graphics processing unit) to process video data like the Kiloview E1 Encoder, while a software encoder is a program such as OBS that runs on a computer platform using the CPU for processing the stream data.
This means HD video encoding with software will never make friends with computer of low-power CPU – it may not decode smoothly or affect other tasks running, especially for low-configuration computers. Moreover, with 4k and H.265’s overwhelming development, CPU decoding could not afford to encode such videos.
Unlike computers, hardware encoders are dedicated to doing one task, which is to encode your video/ audio. There is less risk of a hardware encoder freezing during production whereas a computer is more susceptible to freezing and crashes. Additionally, you don’t have to worry about CPU usage limits, memory, and network security problems when using a hardware encoder.